Actuator Surface Model
The aerodynamic solution computed in the first section was intended to be a mid-low fidelity simulation, which modeled the wing using an actuator line model (ALM). The ALM places all the surface vorticity associated with lift at the quarter chord of the wing, while placing all the trailing bound vorticity at the three-quarter chord, as shown here:
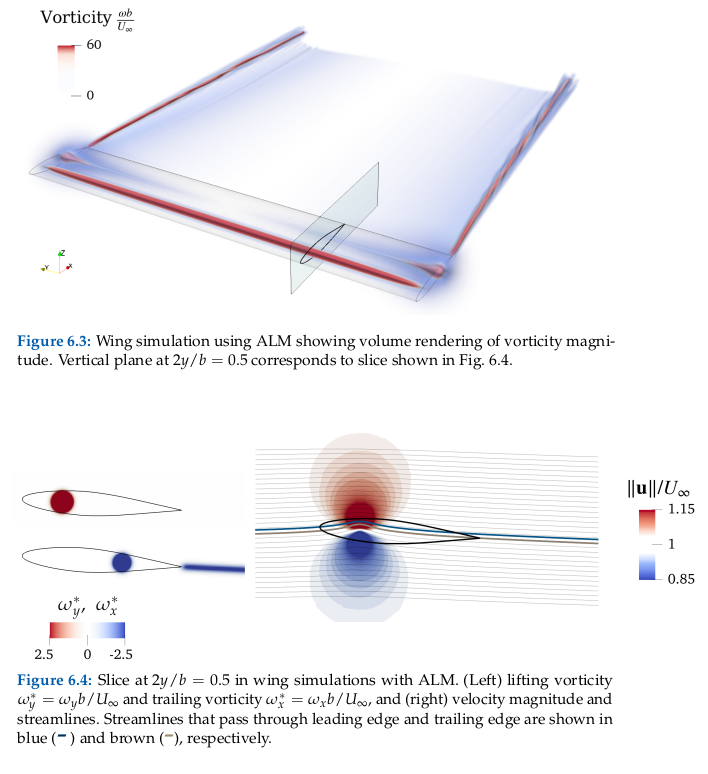
The ALM is very accurate for isolated wings and even cases with mild wake interactions. However, for cases with stronger wake interactions (e.g., a wake directly impinging on the wing surface), the ALM can lead to unphysical results as the flow tends to cross the airfoil centerline. To address this, we have developed an actuator surface model (ASM) to embed the wing surface in the LES domain and better represent the physics.
The ASM spreads the surface vorticity following a pressure-like distribution. This produces a velocity field at the wing surface that minimizes the mass flow that crosses the airfoil centerline, thus better representing a solid surface:
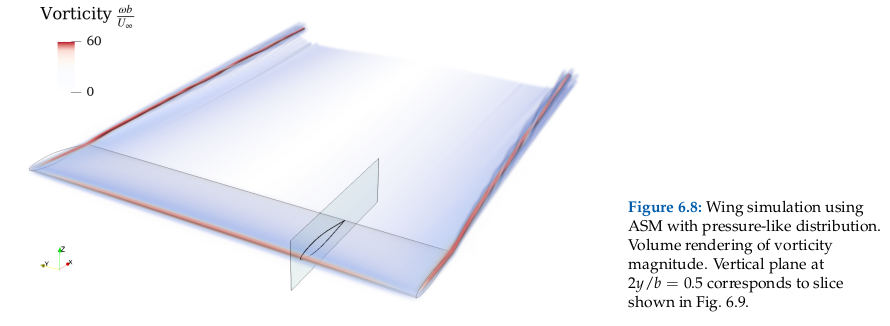
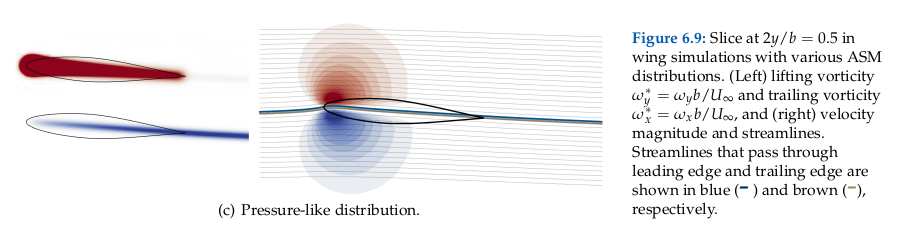
For an in-depth discussion of the actuator models implemented in FLOWUnsteady, see Chapter 6 in Alvarez' Dissertation[2] (also published in Alvarez & Ning, 2023[3]).
In order to activate the actuator surface model, we define the following parameters:
thickness_w = 0.15 # Wing airfoil thickness t/c
# ---------- Vortex sheet parameters ---------------
vlm_vortexsheet = true # Whether to spread the wing circulation as a vortex sheet
vlm_vortexsheet_overlap = 2.125 # Overlap of the particles that make the vortex sheet
vlm_vortexsheet_distribution = uns.g_pressure # Distribution of the vortex sheet
sigma_vlm_surf = b/100 # Smoothing radius of lifting bound vorticity
vlm_vortexsheet_sigma_tbv = thickness_w*(b/ar) / 100 # Smoothing radius of trailing bound vorticity
vlm_vortexsheet_maxstaticparticle = 1000000 # How many particles to preallocate for the vortex sheet
# ---------- Force calculation parameters ----------
KJforce_type = "regular" # KJ force evaluated at middle of bound vortices
# KJforce_type = "averaged" # KJ force evaluated at average vortex sheet
# KJforce_type = "weighted" # KJ force evaluated at strength-weighted vortex sheet
include_trailingboundvortex = false # Include trailing bound vortices in force calculations
include_freevortices = false # Include free vortices in force calculation
include_freevortices_TBVs = false # Include trailing bound vortex in free-vortex force
include_unsteadyforce = true # Include unsteady force
add_unsteadyforce = false # Whether to add the unsteady force to Ftot or to simply output it
include_parasiticdrag = true # Include parasitic-drag force
add_skinfriction = true # If false, the parasitic drag is purely form, meaning no skin friction
calc_cd_from_cl = false # Whether to calculate cd from cl or effective AOA
wing_polar_file = "xf-rae101-il-1000000.csv" # Airfoil polar for parasitic dragThen we use a custom-defined function for calculating aerodynamic forces that uses the vortex sheet:
# ---------- Aerodynamic forces --------------
forces = []
# Calculate Kutta-Joukowski force
kuttajoukowski = uns.generate_aerodynamicforce_kuttajoukowski(KJforce_type,
sigma_vlm_surf, sigma_rotor_surf,
vlm_vortexsheet, vlm_vortexsheet_overlap,
vlm_vortexsheet_distribution,
vlm_vortexsheet_sigma_tbv;
vehicle=vehicle)
push!(forces, kuttajoukowski)
# Free-vortex force
if include_freevortices
freevortices = uns.generate_calc_aerodynamicforce_freevortices(
vlm_vortexsheet_maxstaticparticle,
sigma_vlm_surf,
vlm_vortexsheet,
vlm_vortexsheet_overlap,
vlm_vortexsheet_distribution,
vlm_vortexsheet_sigma_tbv;
Ffv=uns.Ffv_direct,
include_TBVs=include_freevortices_TBVs
)
push!(forces, freevortices)
end
# Force due to unsteady circulation
if include_unsteadyforce
unsteady(args...; optargs...) = uns.calc_aerodynamicforce_unsteady(args...; add_to_Ftot=add_unsteadyforce, optargs...)
push!(forces, unsteady)
end
# Parasatic-drag force (form drag and skin friction)
if include_parasiticdrag
parasiticdrag = uns.generate_aerodynamicforce_parasiticdrag(wing_polar_file;
read_path=joinpath(data_path, "airfoils"),
calc_cd_from_cl=calc_cd_from_cl,
add_skinfriction=add_skinfriction,
Mach=speedofsound!=nothing ? magVref/speedofsound : nothing)
push!(forces, parasiticdrag)
end
# Stitch all the forces into one function
function calc_aerodynamicforce_fun(vlm_system, args...; per_unit_span=false, optargs...)
# Delete any previous force field
fieldname = per_unit_span ? "ftot" : "Ftot"
if fieldname in keys(vlm_system.sol)
pop!(vlm_system.sol, fieldname)
end
Ftot = nothing
for (fi, force) in enumerate(forces)
Ftot = force(vlm_system, args...; per_unit_span=per_unit_span, optargs...)
end
return Ftot
endThis custom-defined force needs to be passed to uns.generate_monitor_wing:
monitor_wing = uns.generate_monitor_wing( ...
include_trailingboundvortex=include_trailingboundvortex,
calc_aerodynamicforce_fun=calc_aerodynamicforce_fun,
...
)Finally, pass the following keyword arguments to uns.run_simulation:
# ------------- 5) RUN SIMULATION ------------------------------------------
uns.run_simulation( ...
vlm_vortexsheet=vlm_vortexsheet,
vlm_vortexsheet_overlap=vlm_vortexsheet_overlap,
vlm_vortexsheet_distribution=vlm_vortexsheet_distribution,
vlm_vortexsheet_sigma_tbv=vlm_vortexsheet_sigma_tbv,
max_static_particles=vlm_vortexsheet_maxstaticparticle
...
)The next section shows an example on how to set up and run a simulation using the actuator surface model.
- 2E. J. Alvarez (2022), "Reformulated Vortex Particle Method and Meshless Large Eddy Simulation of Multirotor Aircraft," Doctoral Dissertation, Brigham Young University. [VIDEO] [PDF]
- 3E. J. Alvarez and A. Ning (2023), "Meshless Large-Eddy Simulation of Propeller–Wing Interactions with Reformulated Vortex Particle Method," Journal of Aircraft. [DOI][PDF]